AP Chem Unit 5 Progress Check MCQ: Mastering Equilibrium and Beyond embarks on a journey through the intricacies of chemical equilibrium, a fundamental concept that governs countless chemical processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the principles of equilibrium, its applications, and the factors that influence its delicate balance.
From Le Chatelier’s principle to acid-base equilibria, solubility equilibria to redox reactions, this progress check empowers students with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of equilibrium chemistry. By exploring equilibrium calculations, ICE tables, and the behavior of strong and weak acids and bases, learners gain a profound understanding of how chemical systems respond to changes in their environment.
Chemical Equilibrium: Ap Chem Unit 5 Progress Check Mcq
Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction occur at the same rate, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products. This state is characterized by a constant equilibrium constant, which is a measure of the relative amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium.
Key Concepts
- The fundamental principles underlying chemical equilibrium include the law of mass action and the concept of free energy.
- Le Chatelier’s principle predicts the shift in equilibrium position when a stress is applied to the system.
- Factors that affect the position of equilibrium include temperature, pressure, and concentration.
Equilibrium Calculations
Equilibrium concentrations can be calculated using the equilibrium constant expression. ICE tables (initial, change, equilibrium) are a useful tool for solving equilibrium problems involving gases, solids, and solutions.
Acid-Base Equilibria
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Strong acids and bases completely dissociate in water, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate. Buffer solutions resist changes in pH and are used in a variety of applications.
Solubility Equilibria
Solubility is the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a solvent. The solubility product constant (Ksp) is a measure of the solubility of an ionic compound. Factors that affect solubility include temperature and the common ion effect.
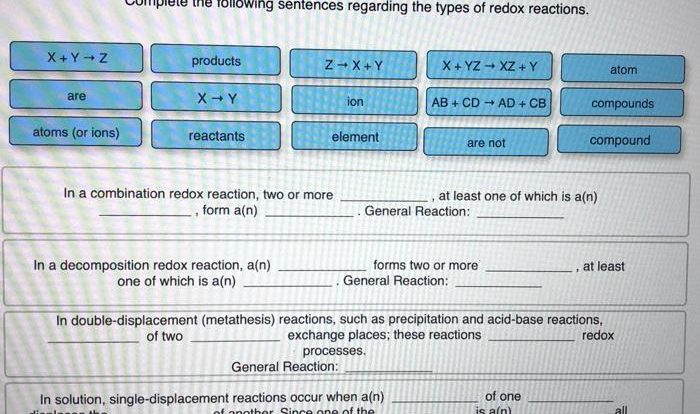
Redox Reactions, Ap chem unit 5 progress check mcq
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons. Oxidizing agents cause other substances to lose electrons, while reducing agents cause other substances to gain electrons. Electrode potentials can be used to predict the spontaneity of redox reactions.
FAQs
What is the significance of Le Chatelier’s principle?
Le Chatelier’s principle provides a framework for predicting how equilibrium systems respond to external changes, allowing chemists to manipulate conditions to favor desired outcomes.
How are ICE tables used in equilibrium calculations?
ICE tables (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) offer a structured approach to solving equilibrium problems by tracking the changes in concentrations of reactants and products as the system reaches equilibrium.
What is the relationship between pH and acid-base equilibria?
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, and it is inversely related to the concentration of hydrogen ions. Acid-base equilibria involve the interconversion of acids and bases, influencing the pH of the system.