Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of genetics with our comprehensive practice with monohybrid Punnett squares worksheet answer key. This invaluable resource empowers you to unravel the intricacies of genetic inheritance, unraveling the mysteries of dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous conditions, and the remarkable power of Punnett squares in predicting genetic outcomes.
Prepare to delve into the fascinating world of genetic inheritance, where the secrets of life’s blueprint await your discovery.
Our meticulously crafted worksheet provides a step-by-step guide to constructing Punnett squares, ensuring a thorough understanding of this fundamental genetic tool. We delve into the concepts of genotype and phenotype, empowering you to determine the genetic makeup and observable traits of offspring with remarkable precision.
Probability calculations come to life as we explore the likelihood of inheriting specific alleles and genotypes, equipping you with the knowledge to predict genetic outcomes with confidence.
Monohybrid Punnett Squares
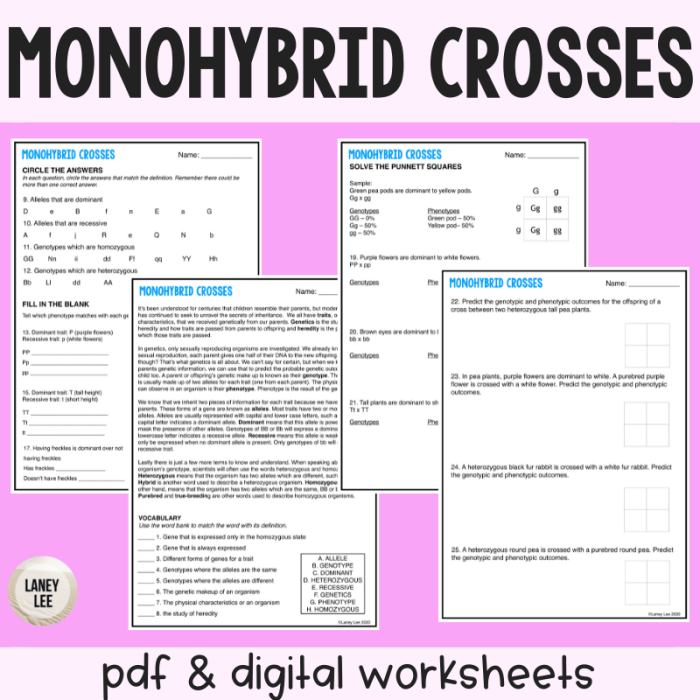
A monohybrid Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents who differ in a single gene. It is a valuable tool for understanding the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
Definitions
- Dominant allele:An allele that masks the expression of a recessive allele when both are present in an individual’s genotype.
- Recessive allele:An allele that is only expressed in an individual’s phenotype when two copies of the allele are present in the genotype.
- Homozygous:Having two identical alleles for a particular gene.
- Heterozygous:Having two different alleles for a particular gene.
Punnett Square Construction
To create a monohybrid Punnett square, follow these steps:
- Write the alleles of one parent along the top of the square and the alleles of the other parent along the side.
- Separate the alleles for each parent so that each allele is in its own box.
- Fill in the boxes of the square by combining the alleles from the top and side.
Genotype and Phenotype
The genotype of an individual refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while the phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an individual.
Using a Punnett square, you can determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring by examining the combinations of alleles in the boxes.
Probability Calculations
Punnett squares can be used to calculate the probability of inheriting specific alleles and genotypes.
The probability of inheriting a particular allele is equal to the number of boxes in the Punnett square that contain that allele divided by the total number of boxes in the square.
The probability of inheriting a particular genotype is equal to the number of boxes in the Punnett square that contain that genotype divided by the total number of boxes in the square.
Applications, Practice with monohybrid punnett squares worksheet answer key
Punnett squares are used in a variety of real-world scenarios, including:
- Predicting the genetic outcomes of crosses in plants, animals, and humans.
- Determining the probability of inheriting specific genetic disorders.
- Understanding the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
FAQ Resource: Practice With Monohybrid Punnett Squares Worksheet Answer Key
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
A Punnett square is a visual tool used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What is the difference between a homozygous and a heterozygous genotype?
A homozygous genotype has two identical alleles for a particular gene, while a heterozygous genotype has two different alleles for the same gene.
How can I use a Punnett square to determine the probability of inheriting a specific allele?
The probability of inheriting a specific allele is determined by the frequency of that allele in the Punnett square.
