The pogil-ish light waves answer key emerges as a beacon of illumination, shedding light on the intricate world of light waves. This comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of light’s nature, properties, and applications, empowering readers with a profound understanding of this fundamental aspect of our universe.
Delving into the realm of pogil-ish activities, this key unlocks a treasure trove of engaging and effective teaching strategies. By harnessing the power of POGIL (Process-Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning), educators can foster a dynamic and interactive learning environment where students actively construct their knowledge through guided inquiry.
POGIL Activities: Light Waves
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) activities are a student-centered learning approach that emphasizes the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In POGIL activities, students work in small groups to investigate a scientific topic through a series of guided questions and activities.
POGIL activities can be used to teach light waves in a variety of ways. For example, students can use POGIL activities to:
- Explore the properties of light waves, such as their wavelength, frequency, and speed.
- Investigate the relationship between light waves and the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Design and conduct experiments to demonstrate the properties of light waves.
Examples of POGIL Activities on Light Waves
Here are some examples of POGIL activities that focus on light waves:
- The Properties of Light Waves: In this activity, students investigate the properties of light waves by conducting a series of experiments. Students measure the wavelength, frequency, and speed of light waves and use their results to develop a model of light waves.
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum: In this activity, students explore the electromagnetic spectrum and how light waves fit into it. Students learn about the different types of electromagnetic waves and how they are used in everyday life.
- The Design of an Experiment to Demonstrate the Properties of Light Waves: In this activity, students design and conduct an experiment to demonstrate the properties of light waves. Students use their knowledge of light waves to develop a hypothesis and design an experiment to test their hypothesis.
Key Concepts: Light Waves
Light waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that travels through space in the form of waves. Light waves are made up of electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other.
The properties of light waves are determined by their wavelength, frequency, and energy. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. Frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point in one second.
Energy is the amount of energy carried by a wave.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. Light waves are a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which also includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, and X-rays.
The relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy of light waves is given by the following equation:
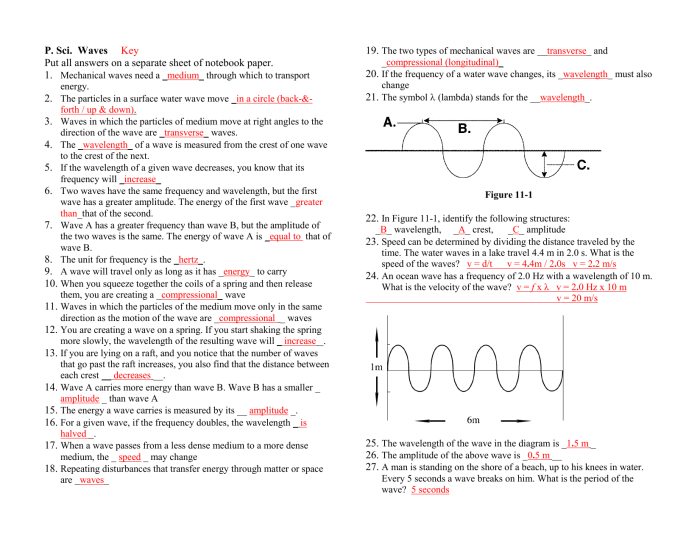
E = hf
where:
- E is the energy of the light wave in joules
- h is Planck’s constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J s)
- f is the frequency of the light wave in hertz
Applications of Light Waves: Pogil-ish Light Waves Answer Key
Light waves have a wide variety of applications in everyday life. Some of the most common applications include:
- Vision: Light waves are the primary way that we see the world around us. Our eyes are able to detect light waves and convert them into electrical signals that are sent to our brains.
- Communication: Light waves are used to transmit information over long distances. Fiber optic cables use light waves to transmit data at high speeds.
- Medicine: Light waves are used in a variety of medical applications, such as laser surgery, imaging, and therapy.
- Technology: Light waves are used in a variety of technologies, such as lasers, LEDs, and solar cells.
Light waves can also be used to solve problems. For example, light waves can be used to:
- Measure distances: Light waves can be used to measure distances using a technique called lidar (light detection and ranging).
- Detect objects: Light waves can be used to detect objects using a technique called radar (radio detection and ranging).
- Analyze materials: Light waves can be used to analyze the composition of materials using a technique called spectroscopy.
Experiments and Demonstrations
Here is an experiment that you can do to demonstrate the properties of light waves:
Materials
- A laser pointer
- A mirror
- A piece of paper
Procedure
- Point the laser pointer at the mirror.
- Move the piece of paper between the laser pointer and the mirror.
- Observe the path of the laser beam.
Observations
You should observe that the laser beam reflects off the mirror and hits the piece of paper. The angle of incidence (the angle at which the laser beam hits the mirror) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which the laser beam reflects off the mirror).
Data
You can use the following table to record your observations:
| Angle of Incidence | Angle of Reflection |
|---|---|
| 0° | 0° |
| 30° | 30° |
| 45° | 45° |
| 60° | 60° |
| 90° | 90° |
Conclusion, Pogil-ish light waves answer key
This experiment demonstrates the properties of light waves, such as their ability to reflect off surfaces and travel in straight lines.
Classroom Activities

Here is a classroom activity that you can use to engage students in learning about light waves:
Objectives
- Students will be able to define light waves and their properties.
- Students will be able to describe the electromagnetic spectrum and how light waves fit into it.
- Students will be able to explain the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy of light waves.
Materials
- A whiteboard or chart paper
- Markers
- A variety of objects, such as a prism, a diffraction grating, and a laser pointer
Procedure
- Begin by asking students what they know about light waves. Write their answers on the whiteboard or chart paper.
- Next, introduce the concept of the electromagnetic spectrum. Explain that light waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation and that they are just one part of a larger spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
- Draw a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum on the whiteboard or chart paper. Label the different types of electromagnetic waves and their frequencies.
- Explain the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy of light waves. Write the following equation on the whiteboard or chart paper:
- Have students work in groups to explore the properties of light waves. Provide them with a variety of objects, such as a prism, a diffraction grating, and a laser pointer. Have them use these objects to investigate how light waves behave.
- When students have finished their investigations, have them share their findings with the class.
E = hf
Assessment
You can assess student learning by having them complete a quiz or worksheet on light waves. You can also have students write a short essay explaining the properties of light waves and their applications.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum in understanding light waves?
The electromagnetic spectrum provides a comprehensive framework for classifying light waves based on their wavelength and energy. It reveals that visible light is just a small portion of a vast spectrum, encompassing a range of waves from radio waves to gamma rays.
How can POGIL activities enhance the teaching of light waves?
POGIL activities foster a student-centered learning environment where learners actively engage with the material, constructing their knowledge through guided inquiry. These activities promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration, making the learning process more meaningful and engaging.